Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a key role in bone strength, immune health, muscle function, and overall well being. Many people rely on eggs as a dietary source of vitamin D, but eggs contain only a modest amount. If you are looking for fish with more vitamin D than an egg, seafood is one of the most powerful and natural options available.
In this guide, you will learn why fish is a superior source of vitamin D, how it compares to eggs, and which six fish provide significantly higher vitamin D levels. You will also find practical tips, nutrition comparisons, and answers to common questions so you can make smarter food choices.
Why Vitamin D Matters for Your Health
Vitamin D supports multiple systems in the body. A deficiency can lead to weak bones, low immunity, fatigue, and long term health risks.
Key benefits of vitamin D include:
- Supporting calcium absorption for strong bones and teeth
- Strengthening the immune system
- Improving muscle strength and balance
- Supporting heart and brain health
- Helping regulate mood and energy levels
While sunlight helps the body produce vitamin D, diet remains a critical source, especially for people who spend little time outdoors.
Vitamin D From Fish vs Egg: A Clear Comparison
A single large egg provides about 40 IU of vitamin D. This is helpful, but it covers only a small portion of daily needs.
In contrast, many types of seafood high in vitamin D provide several times more vitamin D in one serving.
Why fish is better than eggs:
- Fish contains vitamin D naturally, not just fortified amounts
- Fatty fish stores vitamin D in higher concentrations
- Fish also provides omega 3 fatty acids and high quality protein
When comparing vitamin D foods compared to eggs, fish clearly stands out as a more efficient option.
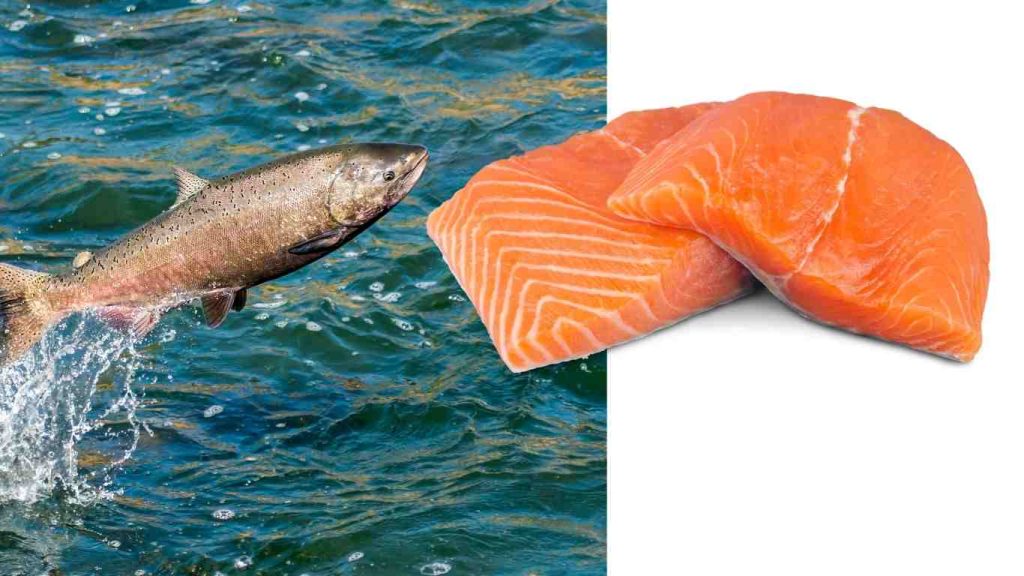
1. Salmon (Wild Caught)
Salmon is widely considered one of the best fish for vitamin D, especially when wild caught.
Vitamin D content
- Wild salmon: 600 to 1000 IU per 100 g
- Farmed salmon: slightly lower but still high
Health benefits
- Excellent source of omega 3 fatty acids
- Supports heart and brain health
- High quality protein for muscle maintenance
How to include salmon
- Grilled with lemon and herbs
- Baked with vegetables
- Added to salads or rice bowls
Salmon easily qualifies as a top choice among vitamin D rich fish.
2. Mackerel
Mackerel is a fatty fish that delivers impressive vitamin D levels along with rich flavor.
Vitamin D content
- Around 360 IU per 100 g
Health benefits
- Supports cardiovascular health
- Helps reduce inflammation
- Improves energy levels
Best ways to eat mackerel
- Lightly grilled
- Smoked (in moderation)
- Pan cooked with minimal oil
Mackerel is an affordable and accessible option for those seeking fish high in vitamin D.
3. Sardines
Sardines may be small, but they are packed with nutrients.
Vitamin D content
- Around 270 IU per 100 g
Why sardines are a smart choice
- Rich in calcium and vitamin B12
- Low in mercury
- Convenient canned option
Serving ideas
- On whole grain toast
- Mixed into salads
- Added to pasta dishes
Sardines are one of the most efficient natural sources of vitamin D available.
4. Tuna (Fresh and Canned)
Tuna is popular worldwide and easy to include in daily meals.
Vitamin D content
- Fresh tuna: about 230 IU per 100 g
- Canned tuna: slightly less but still beneficial
Benefits of tuna
- Lean protein source
- Supports muscle recovery
- Easy to prepare
Tips for safe consumption
- Limit intake to avoid excess mercury
- Choose light tuna when possible
Tuna remains a strong contender among seafood high in vitamin D.
5. Herring
Herring is commonly consumed fresh, pickled, or smoked.
Vitamin D content
- Approximately 560 IU per 100 g
Health advantages
- Excellent omega 3 profile
- Supports heart rhythm and circulation
- Helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels
How to enjoy herring
- With boiled potatoes
- In sandwiches
- As part of traditional dishes
Herring provides far more vitamin D than eggs in a single serving.
6. Cod Liver (and Cod Liver Oil)
Cod liver is one of the richest dietary sources of vitamin D.
Vitamin D content
- Cod liver oil: up to 1300 IU per tablespoon
Important notes
- Extremely potent source
- Should be consumed in moderation
- Often recommended as a supplement
Cod liver oil is unmatched when discussing fish with more vitamin D than an egg.
Vitamin D Foods Compared to Eggs: Summary Table
- Egg (1 large): about 40 IU
- Salmon (100 g): up to 1000 IU
- Herring (100 g): about 560 IU
- Mackerel (100 g): about 360 IU
- Sardines (100 g): about 270 IU
- Tuna (100 g): about 230 IU
This comparison clearly shows why fish is the superior dietary source.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need Daily
General guidelines suggest:
- Adults: 600 to 800 IU per day
- Older adults: up to 1000 IU per day
A single serving of vitamin D rich fish can meet or exceed daily requirements.
Best Cooking Methods to Preserve Vitamin D
To retain maximum vitamin D:
- Avoid deep frying
- Use baking, grilling, or steaming
- Cook at moderate temperatures
Proper cooking ensures you get the full benefit of vitamin D from fish vs egg.
Image Optimization Recommendation
Suggested image file name:
- fish-with-more-vitamin-d-than-an-egg.jpg
Suggested ALT text:
- Fish with more vitamin D than an egg including salmon and sardines
Include at least one high quality image near the top of the article.
FAQs
Which fish has more vitamin D than an egg
Salmon, herring, mackerel, sardines, tuna, and cod liver all contain significantly more vitamin D than an egg.
Is fish better than eggs for vitamin D
Yes. Fish provides much higher levels of vitamin D per serving compared to eggs.
Can I get enough vitamin D from food alone
Yes, especially if you regularly eat vitamin D rich fish.
Is canned fish still high in vitamin D
Yes. Sardines and tuna retain much of their vitamin D even when canned.
How often should I eat fish for vitamin D
Two to three servings per week is generally sufficient for most adults.